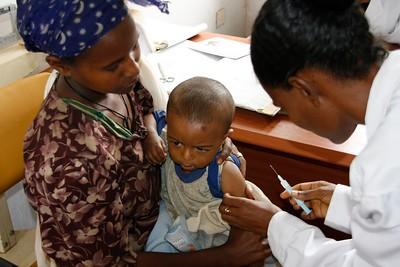
The World Health Organization (WHO) today released its annual global malaria report, which documents 11 million more cases in 2023 compared to 2022, with similar death rates. While malaria remains a serious global health threat, the African region bears the brunt of the disease as the site of 95% of malaria-related deaths.
Overall, an estimated 263 million cases and 597,000 malaria deaths occurred in 2023. This represents about 11 million more cases than in 2022 and nearly the same number of deaths.
But gains are being made towards malaria control in many countries. As of November of this year, 44 countries and 1 territory have been certified malaria-free, the WHO said. In 83 countries where malaria is endemic, 25 report 10 or fewer cases per year. In 2000, only 4 countries reported 10 or fewer cases annually.
Mortality rates drop
Mortality rates from malaria have also dropped, especially in Africa. Since 2015, the African region has seen a 15% drop in mortality rates. However, the region’s current mortality rate of 52.4 deaths per 100,000 population is still more than double the target of 23 deaths per 100,000 population.
Currently, 11 African nations report 70% of the world’s malaria cases (Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Ghana, Mali, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Sudan, United Republic of Tanzania, and Uganda). Ministers of health from the countries pledged renewed support of malaria control efforts earlier this year.
In many of those nations, strides are being made with deployment of new-generation nets, which account for 78% of the 195 million nets delivered to sub-Saharan Africa, up from 59% in 2022. And as of this month, 17 countries have introduced malaria vaccines through routine childhood immunization.
“No one should die of malaria; yet the disease continues to disproportionately harm people living in the African region, especially young children and pregnant women,“ said Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, PhD, WHO director-general. “An expanded package of lifesaving tools now offers better protection against the disease, but stepped-up investments and action in high-burden African countries are needed to curb the threat.“
Hi there, i read your blog from time to time and i own a
similar one and i was just curious if you get a lot of spam comments?
If so how do you prevent it, any plugin or anything you can suggest?
I get so much lately it’s driving me mad so
any help is very much appreciated.
Hi to every body, it’s my first pay a visit of this web site; this webpage includes remarkable and genuinely good data in favor of readers.
Hi there, I enjoy reading through your post.
I like to write a little comment to support you.
Your style is very unique compared to other people I’ve read stuff from.
Thanks for posting when you’ve got the opportunity, Guess
I’ll just bookmark this page.
Howdy! Do you know if they make any plugins to help with Search Engine Optimization? I’m trying to get my blog to rank for some targeted keywords but I’m not seeing very good success.
If you know of any please share. Cheers!
I am really enjoying the theme/design of your site. Do you ever run into any browser compatibility problems?
A couple of my blog audience have complained about my site not operating correctly in Explorer but
looks great in Opera. Do you have any solutions to help fix this problem?
Thanks to my father who informed me concerning this webpage, this
weblog is actually amazing.
mango extract weight loss https://otvetnow.ru medical whistleblower
Hi! This post could not be written any better! Reading through
this post reminds me of my good old room mate! He always kept chatting about this.
I will forward this write-up to him. Pretty sure he
will have a good read. Thanks for sharing!
https://askoff.ru
This site was… how do you say it? Relevant!! Finally I’ve
found something that helped me. Thanks!
Awesome issues here. I am very satisfied to look your post.
Thanks so much and I am looking ahead to contact you.
Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
If you want to take much from this paragraph
then you have to apply such techniques to your won weblog.
I was suggested this website by my cousin. I am not sure whether this post
is written by him as no one else know such detailed about my problem.
You are incredible! Thanks!
I read this paragraph completely on the topic of the difference of hottest and earlier technologies, it’s awesome article.
Hey I know this is off topic but I was wondering if you knew of any widgets I could add to
my blog that automatically tweet my newest twitter updates.
I’ve been looking for a plug-in like this for quite some time and was hoping maybe you would have some experience with something like this.
Please let me know if you run into anything. I truly enjoy reading your blog and
I look forward to your new updates.
After looking at a number of the blog posts on your web page,
I really appreciate your technique of blogging. I
added it to my bookmark website list and will be checking back in the
near future. Take a look at my website as well
and let me know how you feel.